Planning & construction
The planning of photovoltaic systems (PV systems) is a complex process that requires both technical expertise and careful preparation. The substructure, the creation of customised drawings and detailed parts lists are particularly important. These elements are crucial for the efficient and safe installation of PV systems and the long-term performance and reliability of the system.
Planning of PV systems
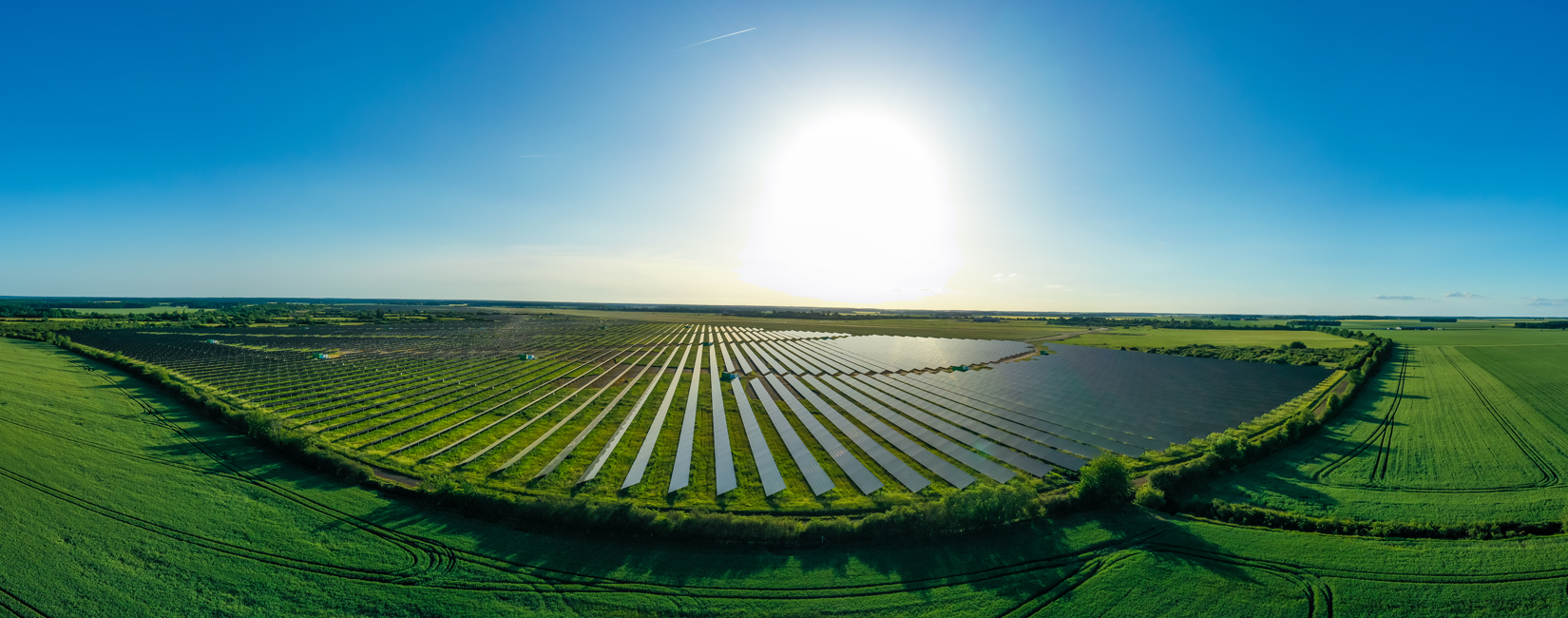
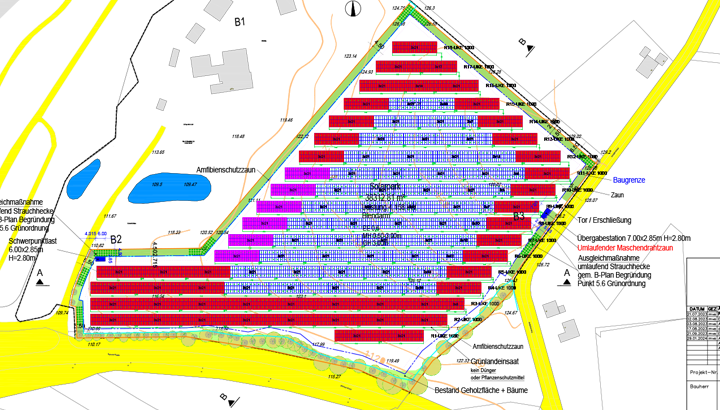
The planning of ground-mounted and agricultural PV systems differs from roof mounting and must take specific requirements into account:
- Site analysis: The design of the system must take into account the specifics of the respective site in order to guarantee efficiency.
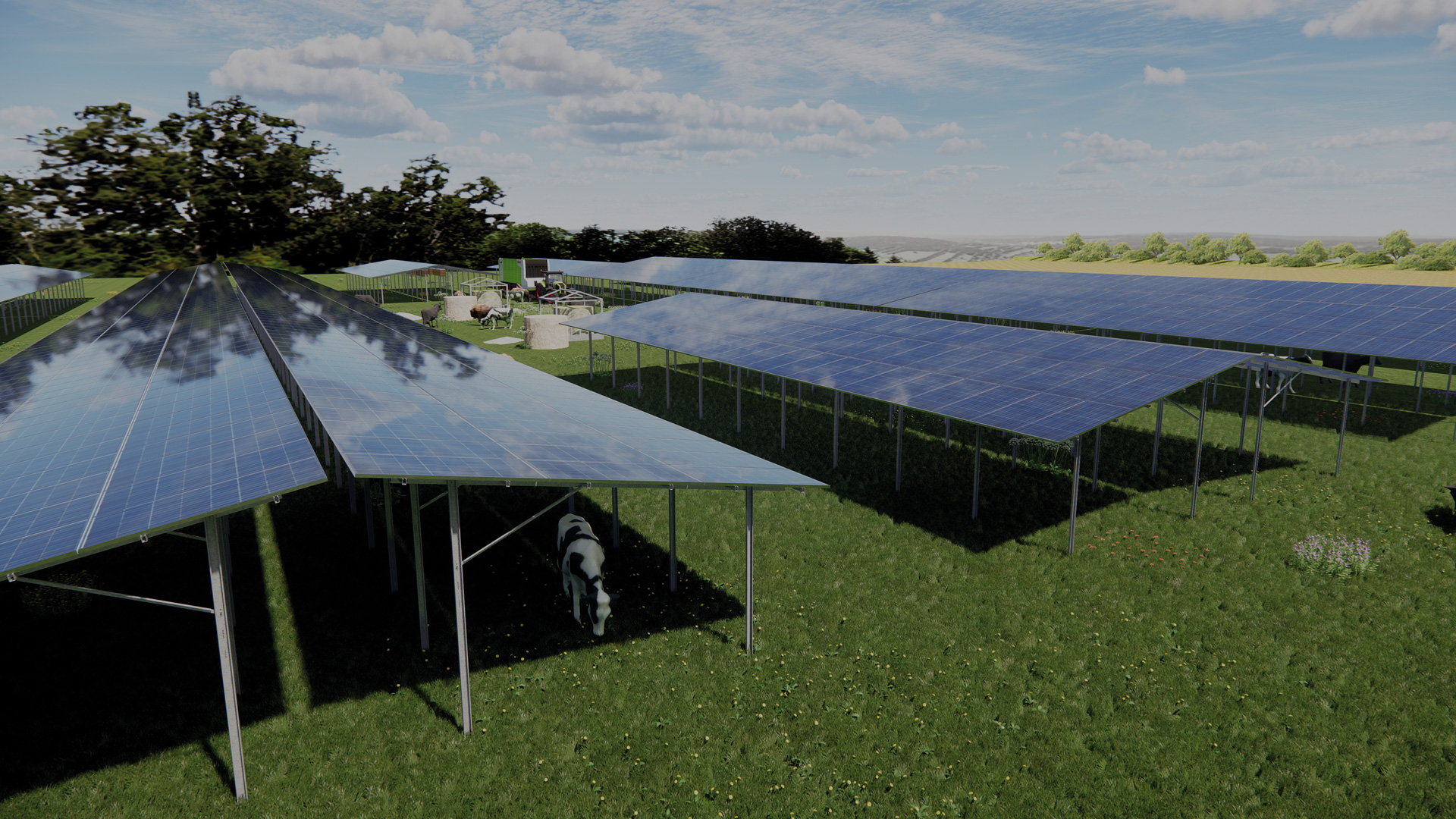
- Conflicts of use: In the case of agrivoltaic systems, the subsequent agricultural use must not conflict with the installed systems.
- Regulatory requirements: Compliance with DIN standards, the Eurocodes and other building regulations is crucial.
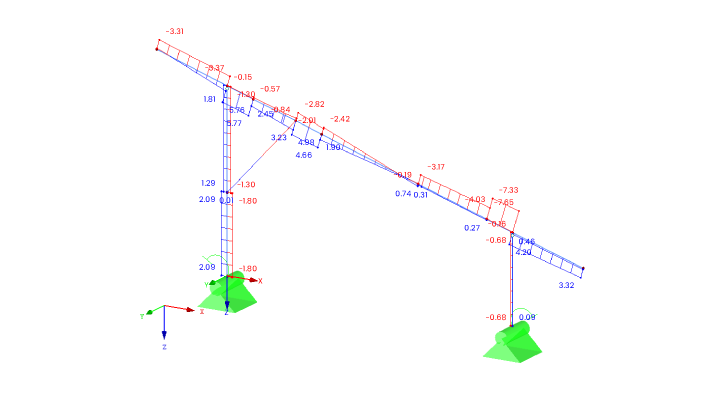
The substructure
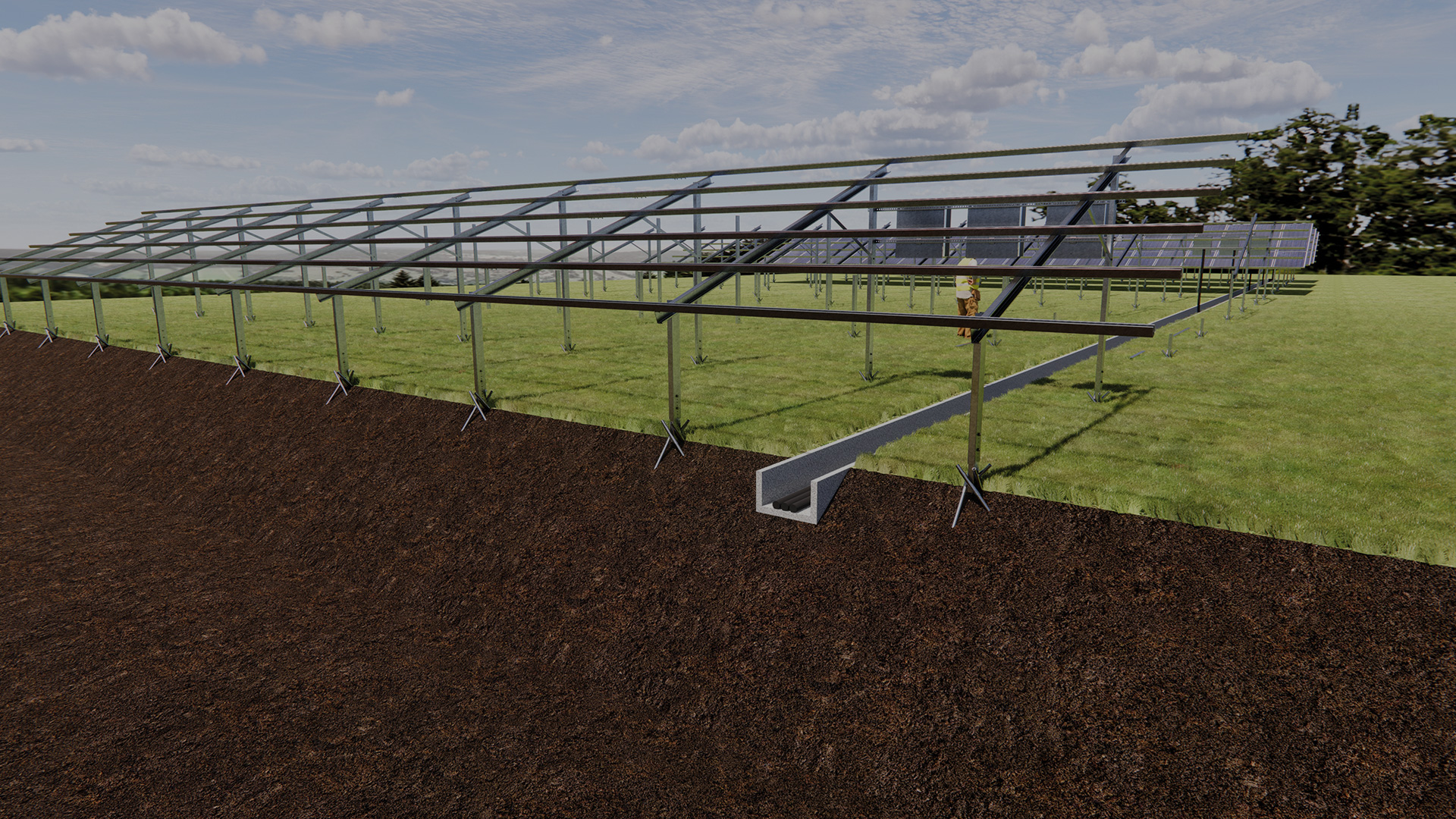
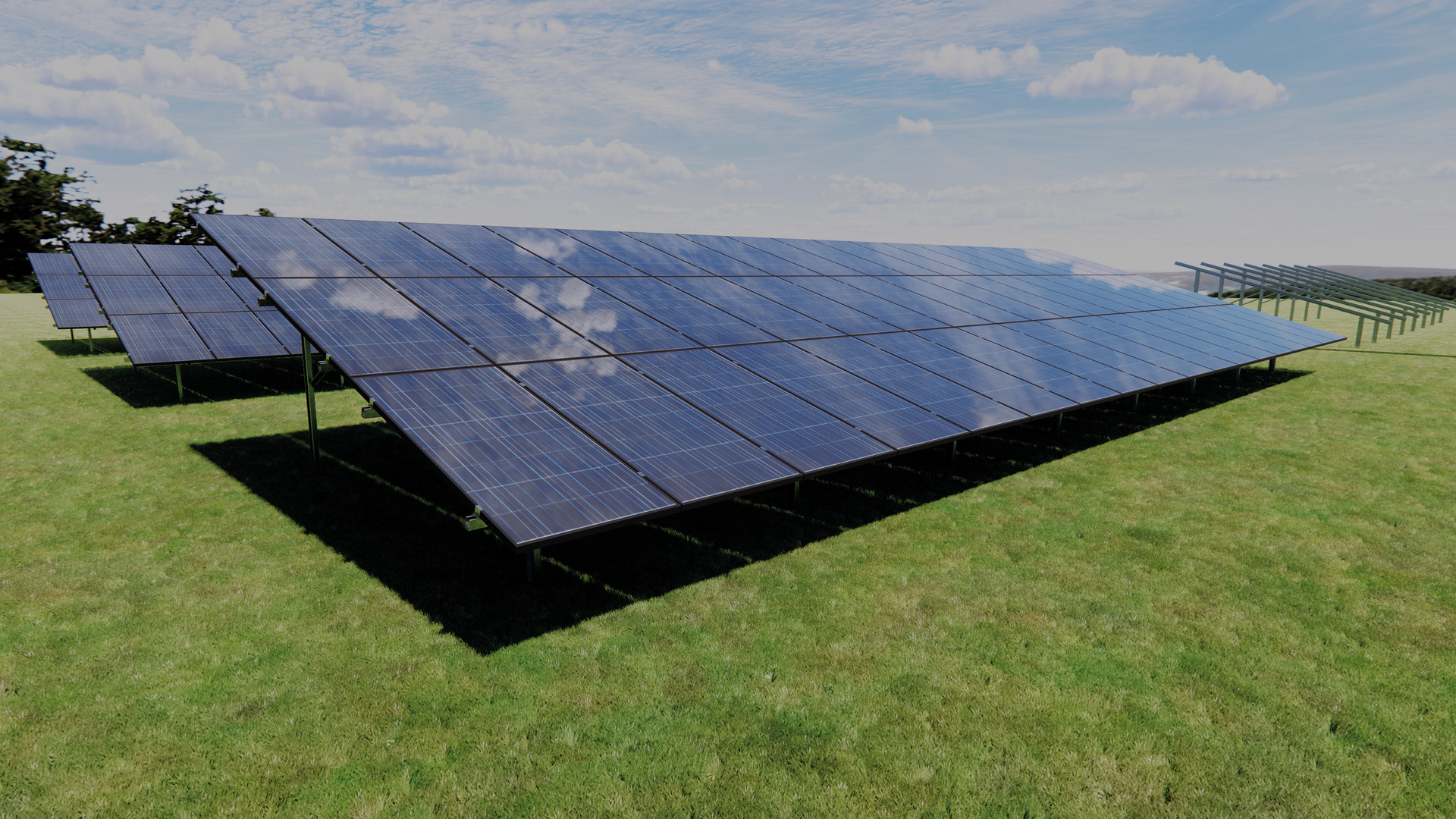
The substructure for ground-mounted PV systems must be robust and durable in order to meet the specific challenges of ground-mounted systems:
- Stability and anchoring: The substructure must be stable and securely anchored in the ground. This can be achieved using post foundations, concrete foundations or screw foundations, depending on the ground conditions.
- Weather resistance: The structure must be able to withstand extreme weather conditions, including strong winds, snow and rain. Corrosion protection measures are therefore essential.

Drawings
- Detailed construction plans: Each component of the substructure is drawn in detail, including the exact dimensions, materials, connections and anchoring in the ground.
- Consideration of the site conditions: The drawings must take into account the specific conditions of the installation site, such as the slope of the terrain, obstacles and the route of supply lines.
- Integration with agricultural use: In the case of agrivoltaic projects, the drawings must also take into account the parallel use of the land for agricultural purposes, such as the height of the modules above the ground for growing crops or the passageways for agricultural machinery.
Creation of bills of materials
The bill of materials (BOM) is a central document for the planning and realisation of PV systems. It ensures that all required materials and components are available:
- Complete listing of all components: Every component, from the main structures to the smallest fastening elements, must be listed in detail.
- Quantity determination: The exact number of components required is determined in order to avoid material bottlenecks during the construction phase.
- Material procurement: The parts list serves as a basis for the procurement of materials and facilitates co-operation with suppliers.
- Cost control: A detailed bill of materials allows material costs to be precisely calculated and monitored, which is crucial for project budget planning.

Customised
- Customised planning: Each system is planned according to the specific needs of the customer and the local conditions. This also includes taking agricultural requirements into account.
- Flexible construction: The substructure and the overall solution must be flexible enough to adapt to different types of terrain and utilisation concepts.
- Adaptation to future requirements: The planning should also take into account future expansions or changes to ensure the longevity and scalability of the system.
Planning
The planning of ground-mounted and agricultural photovoltaic systems requires comprehensive and careful preparation. The substructure, the creation of customised drawings and detailed parts lists are crucial to the success of a PV project. These elements ensure that the systems are safe, efficient and durable and meet the specific requirements of the project. Tailor-made planning and implementation can optimise the use of solar energy and make a sustainable contribution to energy supply and agricultural use.

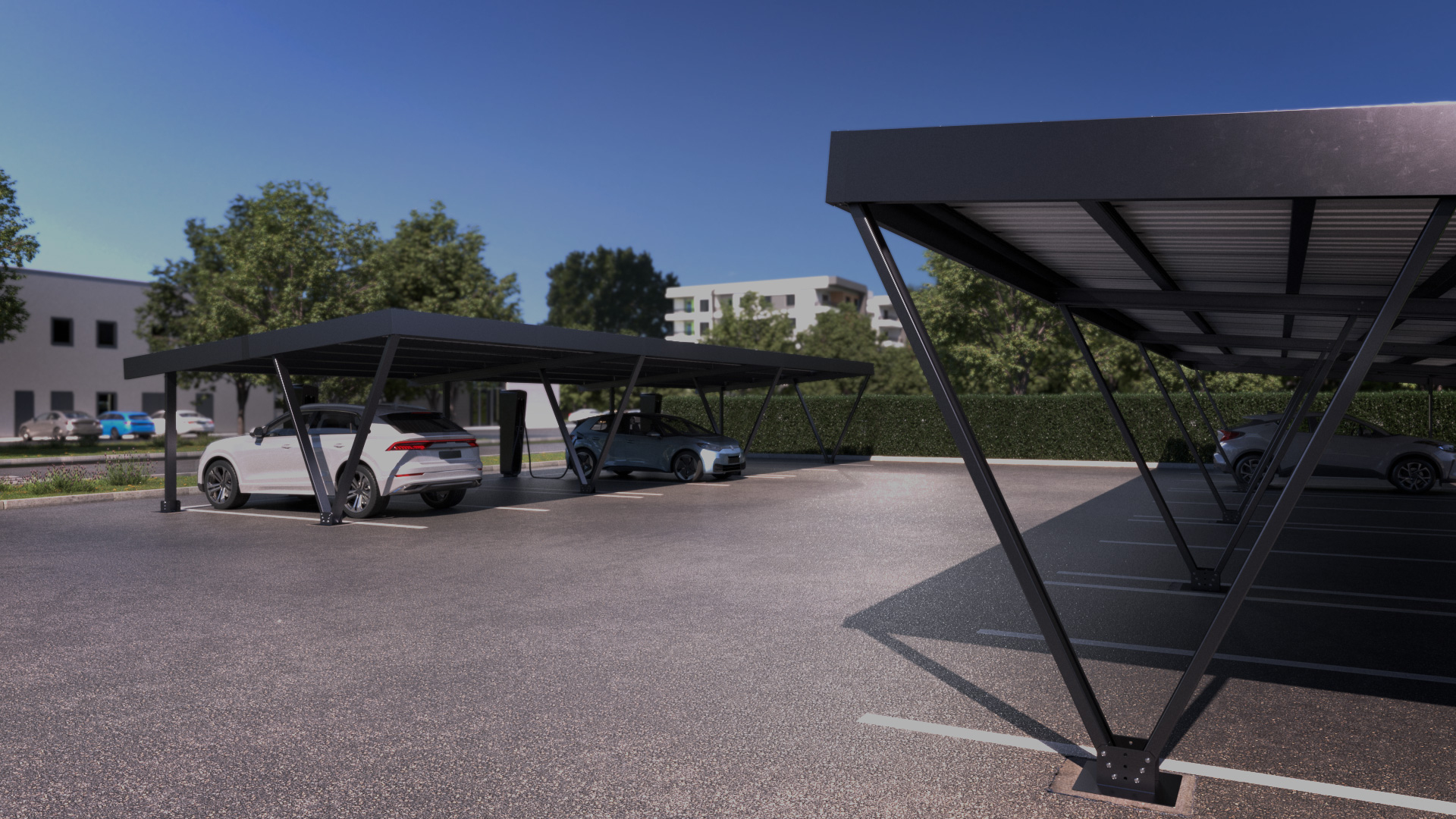
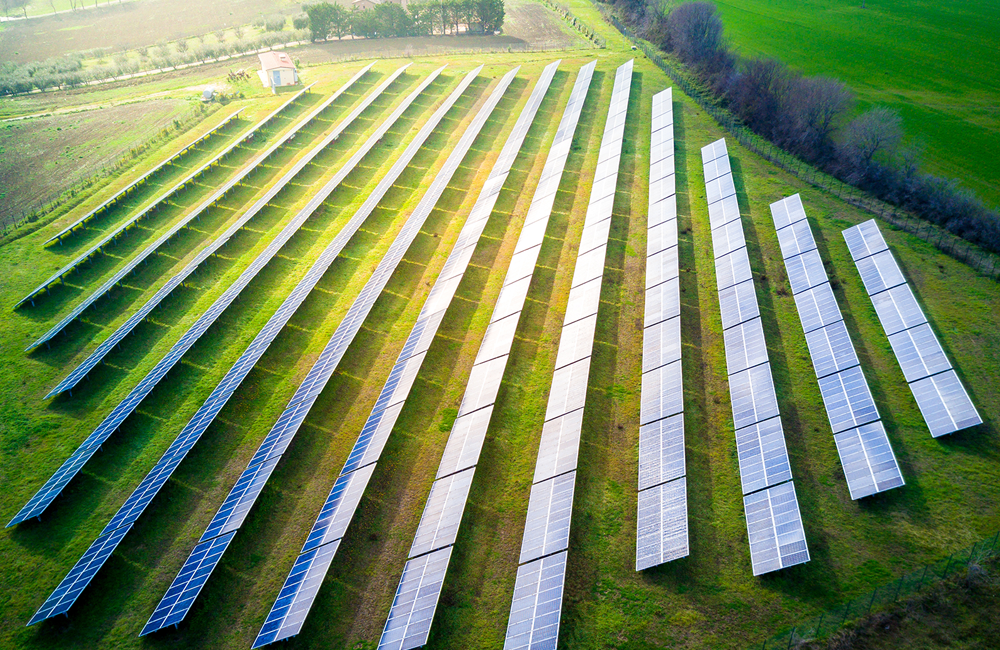
Innovative PV solutions at a glance
Take a look at our latest solutions for installing photovoltaic systems. Whether for facades, agricultural applications or ground-mounted systems, our well-designed mounting systems enable fast, safe and economical implementation. Thanks to modular concepts and high-quality materials, our systems can be flexibly adapted to a wide range of applications.